

The cooling solution for rail transit systems needs to comprehensively consider the needs of vehicle power systems, electronic equipment, braking systems, and passenger comfort.
1. Power system cooling
1.1 Traction system heat dissipation
Liquid cooling technology: For high-power equipment such as IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) and traction converters, a water-cooled or oil cooled circulation system is used to dissipate heat through a radiator.
Air cooling technology: Suitable for low to medium power scenarios, it utilizes forced air cooling (such as high-speed fans) or natural convection for heat dissipation.
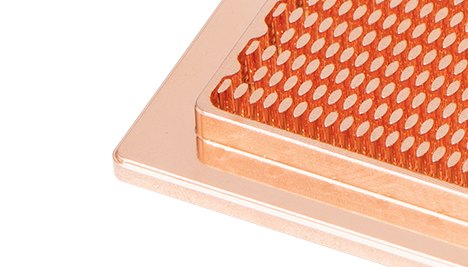
Heat pipe technology: Utilizing the efficient thermal conductivity of heat pipes, heat is quickly conducted from local high-temperature areas to heat sinks or external environments.
1.2 Energy storage system heat dissipation (such as batteries, supercapacitors)
Liquid cooling/phase change cooling: Design liquid cooling plates or phase change materials (PCM) for battery modules to accurately control temperature (such as 20-40 ℃).
Air cooling optimization: Improve air circulation efficiency through channel design, combined with BMS (Battery Management System) real-time monitoring of temperature distribution.
Thermal insulation material: use materials such as aerogel around the battery pack to prevent the impact of external high temperature.
2. Cooling of the braking system
Regenerative braking technology: reduces the heat generated by traditional mechanical braking (energy is recovered to the grid or energy storage device).
Forced air-cooled brake discs: By designing ventilated brake discs and air ducts, the heat dissipation efficiency is improved.
High temperature resistant materials: Use ceramic based composite materials or carbon fiber brake discs to reduce the risk of thermal degradation.
3. Cabin environment control
Optimization of air conditioning system:
Variable frequency compressor technology: dynamically adjust the cooling capacity according to the load to reduce energy consumption.
Distributed air supply: By designing multiple air vents on the top and side walls, the uniformity of airflow is improved.
Fresh air and waste heat recovery: using heat exchangers to recover cold/heat from exhaust air, reducing air conditioning load.
4. Heat dissipation of electronic devices
Cabinet level heat dissipation:
Cold plate liquid cooling: Design customized liquid cooling modules for vehicle control cabinets and communication equipment.
Design of flow hood: Optimize the layout of air ducts to avoid local hotspots.
High thermal conductivity material: using graphene heat sinks and metal based composite materials to enhance thermal diffusion efficiency.


Service Hotline
Email: marketing@gootage.com
Kunshan Factory:
+86-180 1319 2868
No. 2 Bazimiao Road, Penglang Town, Kunshan Development Zone, Jiangsu Province
Yancheng Factory:
+86-188 5169 8737
No. 38 Hexin Road, Yanlong Street, Yandu District, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province
