

Artificial intelligence chips and related hardware generate a large amount of heat when performing complex computing tasks, such as training and inference of deep learning models. For example, some artificial intelligence clusters in data centers have extremely high total power consumption and huge heat dissipation requirements due to the simultaneous operation of numerous high computing chips. In pursuit of higher computing performance, artificial intelligence devices often integrate a large number of computing cores, storage units, and other high-density components in a limited space, resulting in heat concentration and increased difficulty in heat dissipation. Like some artificial intelligence acceleration cards, chips and other components are tightly arranged, making it difficult for heat to dissipate quickly.
Direct liquid cooling: Spray or soak the coolant directly onto the heating components, such as artificial intelligence chips, and use the high specific heat capacity of the liquid to directly remove heat. The heat dissipation efficiency is extremely high, but it requires high compatibility of the coolant and system sealing. Some high-performance artificial intelligence supercomputers may adopt this approach.
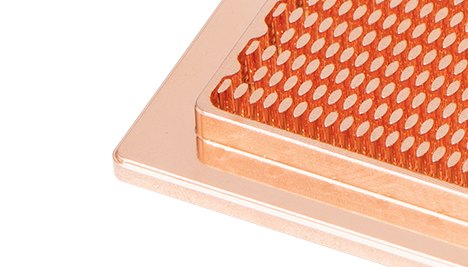
Indirect liquid cooling: By contacting the liquid cooling plate and other components with the heat source, the coolant circulates inside the liquid cooling plate to remove heat. This method is relatively easier to implement and maintain compared to direct liquid cooling, and is commonly used in artificial intelligence server cabinets in data centers, which can effectively reduce the overall temperature of the servers.


Service Hotline
Email: marketing@gootage.com
Kunshan Factory:
+86-180 1319 2868
No. 2 Bazimiao Road, Penglang Town, Kunshan Development Zone, Jiangsu Province
Yancheng Factory:
+86-188 5169 8737
No. 38 Hexin Road, Yanlong Street, Yandu District, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province
